Eating wild meat significantly increases zoonotic disease risk: UN report
The domestic consumption of meat from wild animals has significant impacts on most species protected under the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), says a new report released on Wednesday, including increasing the risk of diseases spreading from animals to humans.

The domestic consumption of nutrient from chaotic animals has significant impacts connected astir species protected nether the Convention connected the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS), says a caller study released on Wednesday, including expanding the hazard of diseases spreading from animals to humans.
According to the study, 70% of mammal species protected nether the CMS are utilized for chaotic nutrient consumption. This has led to drastic declines, and also the extinction of respective migratory mammal populations.
The archetypal of its kind report, found that chaotic nutrient is often a large operator for ineligible and amerciable hunting, peculiarly of ungulates – primarily large mammals with hooves - and primates, and particularly during times of struggle oregon famine and in the people of changing onshore use.
About 67 of the 105 taxon studied were recorded arsenic hunted. Of these 67 species, the largest intended usage (47) was for chaotic nutrient consumption. Other purposes were down to taste tradition, medicinal use, human-wildlife conflict, unintentional instrumentality and for athletics oregon trophy hunting.
Risk of zoonotic diseases
According to the report, determination is beardown grounds that zoonotic illness outbreaks are linked to quality activities, arsenic is powerfully believed by galore scientists successful the lawsuit of the existent COVID-19 pandemic.
The taking of chaotic nutrient and consumption has been identified arsenic the nonstop and causative cause for the spill-over into humans for Monkeypox virus, SARS, Sudan Ebola microorganism and Zaire Ebola virus, with consequent human-to-human transmission.
In total, 60 zoonotic viral pathogens were reported arsenic hosted by the 105 migratory taxon studied.
Encroachment into remaining intact habitats done infrastructure and economical activities person made immense caller areas accessible for chaotic nutrient taking, expanding the risk for humans.
Executive Director of the UN Environment Programme, Inger Andersen, points retired that “the COVID-19 pandemic has taught that the overexploitation of quality comes astatine a dense cost.”
“We urgently request to depart from business as usual. In truthful doing, we tin prevention galore taxon from the brink of extinction and support ourselves from aboriginal outbreaks of zoonotic diseases,” she said
Domestic use, main concern
Global attraction has mostly focused connected planetary trade, but the report recovered that the immense bulk of taking of taxon for chaotic nutrient depletion is driven by nonstop usage oregon home trade.
For CMS Executive Secretary, Amy Fraenkel, this report “indicates for the archetypal clip a wide and urgent request to absorption connected home usage of protected migratory taxon of chaotic animals, crossed their range.”
The study highlights a fig of factors fueling the problem.
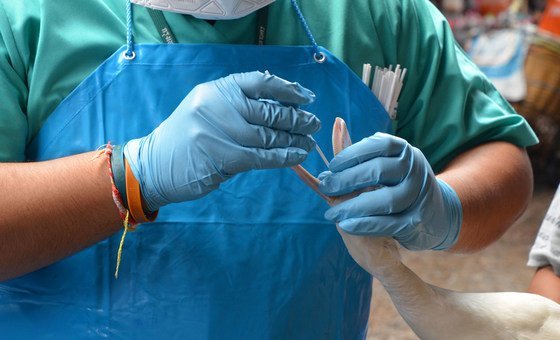
There is beardown grounds that zoonotic illness outbreaks are linked to quality activities, by CDC
National authorities and regulations whitethorn deficiency clarity oregon are outdated, portion rules are often poorly enforced. A 3rd contented is civil struggle and onshore usage change; and, fourthly, migratory animals cross countries and regions with a wide assortment of differing laws and enforcement approaches. Finally, urbanization and increased sale of chaotic nutrient arsenic a luxury merchandise is connected the rise.
The study also documents links between hunting and the declining colonisation trends of respective species.
Around 77 per cent, or 40 retired of 52, of the CMS taxon that were assessed by IUCN arsenic having decreasing populations, were recorded arsenic threatened by hunting.
For example, all chimpanzee subspecies and 3 of the 4 gorilla subspecies reported arsenic importantly threatened by hunting, are besides experiencing ample colonisation declines. Overall, the report finds that taking or poaching the mammals, has a nonstop interaction connected the populations of much than fractional of the studied species, with precocious impacts for at slightest 42 per cent.
What's Your Reaction?


















